Healthcare leaders face a steady stream of rising costs, demanding patients, and complex regulations. Quick fixes help for a while, but they don’t set a steady direction. That’s why clinics and hospitals need a broader game plan to stay competitive and keep care standards high.
Evidence backs this up. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 20-40% of healthcare resources are wasted every year. That means money, staff time, and patient trust vanish before they create value.
That’s where strategic management in healthcare proves its worth. Instead of short bursts of planning, it builds an ongoing rhythm. It involves linking long-term goals with everyday operations, so every decision pushes the organization forward.
Next, we’ll break down how to put this approach into action and keep it running. Let’s take a look.
- TL;DR
- What Strategic Management in Healthcare Means
- Strategic Management vs. Strategic Planning in Healthcare: How Do They Differ?
- Why Strategic Management in Healthcare Is Important?
- Benefits of Strategic Management in Healthcare
- 5 Key Steps to Implement Strategic Management in Healthcare
- Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- Best Practices for Effective Strategic Management in Healthcare
- Bottom Line: Put Your Strategic Management Plan in Motion
- FAQs
TL;DR
Short on time? Here are the main takeaways:
- Strategic management in healthcare keeps hospitals and clinics focused on long-term goals while adapting quickly to change.
- It moves beyond a static document. Real strategy is built on continuous action, clear metrics, and timely course corrections that keep every department aligned.
- Key wins: smarter resource allocation, stronger finances, higher-quality care, and coordinated teams.
- Core moves: run a full situation analysis, set measurable targets, share the plan clearly, track progress, and adjust when needed.
- Common barriers (like tight budgets, staff resistance, and strict compliance rules) are easier to manage when leadership relies on data and well-integrated digital tools.
What Strategic Management in Healthcare Means
Strategic management starts with a simple idea: big goals only matter if they guide daily action. Any organization can use it to stay focused on long-term priorities while adapting when markets or conditions shift.
In the medical field, the stakes are even higher. Strategic management in healthcare gives hospitals and clinics a way to stay focused on patient needs while controlling costs and meeting regulations.
It’s a continuous loop (set objectives, act on them, measure, and adjust), so daily operations keep moving in step with patient expectations and industry demands.
Key Components
Every strong strategy starts with a mission and vision. These guide every choice, from budgeting to patient care standards.
Next come specific goals (for example, cutting wait times or expanding telehealth capacity), followed by a plan to reach them.
The process never stops. It moves through three linked steps:
- Formulation: Identify priorities and decide how to compete and grow.
- Implementation: Convert plans into clear workflows, budgets, and responsibilities.
- Evaluation: Track results and adjust before small issues become major setbacks.
This cycle keeps leadership decisions tied to measurable outcomes.
Core Frameworks and Models
Two proven models give structure to strategic management in healthcare.
The Five Stages of Strategic Management.
This framework walks teams through a logical path:
- Goal setting: Define long-term objectives and success metrics.
- Analysis: Review internal data, market trends, and regulations to ground decisions in facts.
- Strategy formation: Select the best strategic options and map actions to reach goals.
- Implementation: Assign responsibilities, set timelines, and put the plan into motion.
- Monitoring and evaluation: Measure progress, adjust budgets, and fix gaps before they affect patients.
SWOT Analysis
Short for “strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats”, a SWOT analysis is a tool that helps leaders see where they stand.
Internal strengths and weaknesses show what the organization controls, like staff expertise or outdated systems. Meanwhile, external opportunities and threats reveal market and policy pressures.
Together, these insights guide better choices on where to invest and what risks to avoid.
Pro Tip: Using these frameworks keeps the strategy grounded, measurable, and ready to adapt as patient expectations or policies change.
Strategic Management vs. Strategic Planning in Healthcare: How Do They Differ?
It’s true that strategic planning and strategic management go hand in hand, but they play different roles.
Strategic planning is the starting point. It sets objectives, budgets, and timelines, usually for three to five years. Think of it as drawing the map.
Meanwhile, strategic management is an ongoing journey. It checks that the map still matches reality and makes course corrections when new technology, market forces, or patient needs emerge.
The link between the two is critical. A plan without management has no follow-through, and management without a plan has no direction.
When healthcare organizations connect both (using planning to set the course and management to keep it current), they stay on track as conditions change.
Why Strategic Management in Healthcare Is Important?
Healthcare is unpredictable. Costs rise, patient needs change, and regulations keep moving. Without a clear framework, these shifts can knock a clinic off course.
Here’s how strategic management makes the difference:
Align Operations with Long-Term Goals
Day-to-day firefighting can pull teams in different directions. A clear strategy sets a long-term course and ties it to specific actions: budget decisions, staffing, and technology upgrades.
That way, leaders can quickly evaluate every project against those goals and keep resources aimed at measurable results.
Adapt to Industry Changes
Healthcare doesn’t wait. New payment models, telehealth demands, and shifting regulations can change the game in a matter of months. Strategic management helps leaders stay ahead instead of scrambling to react.
By reviewing key metrics often and running small pilot projects, you can spot trends early and adjust services before outside pressures force a big overhaul. An article in IJERPH backs this up, showing that strategic management is critical for sustainable operations as complexity and uncertainty rise.
In other words, steady reviews and data checkpoints are how hospitals and clinics stay ready when the market moves fast. So, they’re not optional.
Improve Patient Outcomes and Quality of Care
Great patient care is built, not improvised. It starts with clear targets like lowering readmission rates or boosting follow-ups for chronic conditions.
After that, it links those targets to daily routines: how appointments are scheduled, how staff communicate, and how technology supports treatment. The payoff is fewer errors, shorter waits, and consistent care no matter who’s on shift.
As an article published in the Multidisciplinary Science Journal notes:
“Strategic management within the healthcare domain assumes a pivotal role in the pursuit of strategic decision-making and the attainment of organizational objectives aimed at enhancing healthcare service quality.”
Benefits of Strategic Management in Healthcare
Done right, strategic management delivers hard results across finances, risk, and team performance. Those benefits include:
Better Resource Allocation
Budgets and staff time are limited, so every choice has to matter. In those cases, strategic management helps leaders focus resources where they have real impact.
Teams look at patient demand alongside current capacity to see which services deserve more support and which can scale back. The payoff is steady, high-quality care, without stretching people or money too thin.
Key Insight: A BMC Health Services Research review showed that public health sectors use strategic planning to lower costs, improve quality, ensure access, and direct resources where they matter most. Clinics and hospitals using the same approach can meet patient needs and stay financially stable.
Improved Risk Management
Unexpected events, from supply chain issues to sudden regulation changes, can disrupt care in hours.
In such scenarios, strategic management builds risk reviews into every stage. That way, leaders can identify weak spots early, assign contingency plans, and keep operations running when emergencies hit.
Stronger Financial Sustainability
Margins are tight in healthcare, so every dollar counts. Keeping investments and daily operations tied to strategic goals helps steady revenue and support growth.
With this approach, leaders can improve billing, manage purchasing costs, and pilot new services, building financial strength as the organization grows.
Enhanced Team Collaboration
A plan only works if the people delivering care own it. With strategic management, leadership, and frontline staff will be in the same conversation through regular check-ins, clear metrics, and open reporting.
That way, everyone sees how their work supports shared objectives, and this builds accountability and trust.
Key Insight: A study at the University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital found that a 1% improvement in strategic management practices led to roughly 40–43% gains in organizational performance. Those gains showed up in several areas. Time management improved, budget efficiency strengthened, and employee satisfaction increased.
5 Key Steps to Implement Strategic Management in Healthcare
Putting strategic management into action in healthcare takes more than one meeting. It needs a clear set of steps that turn big goals into daily practice.
Here’s how to move from plan to execution:
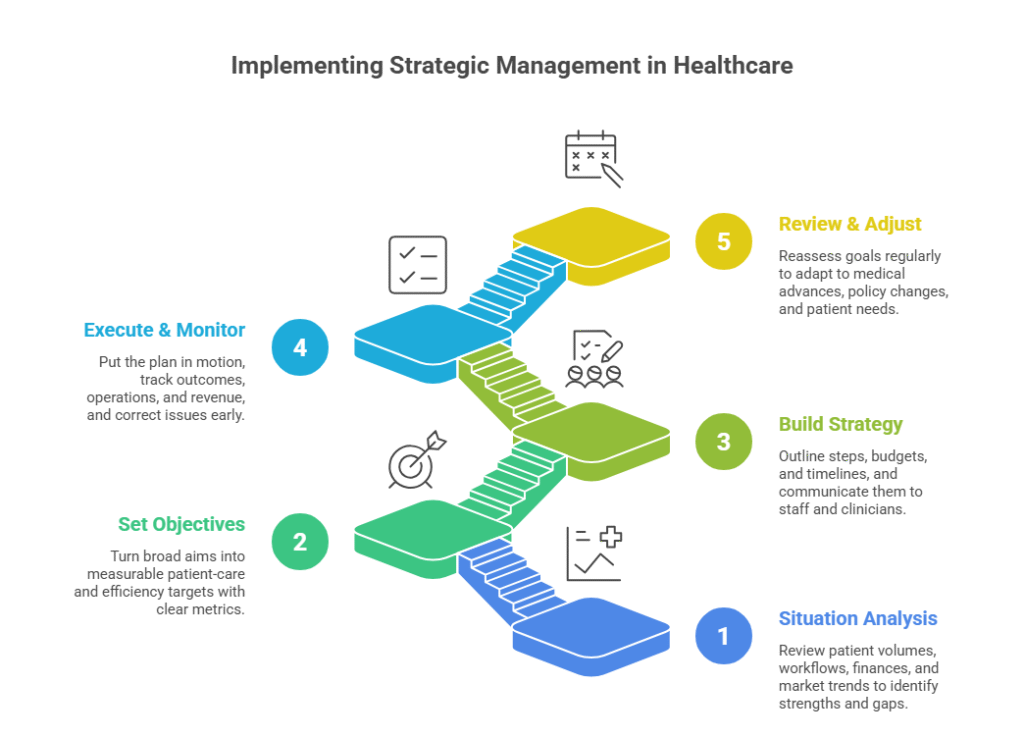
1. Conduct a Thorough Situation Analysis
Start by getting a clear view of where you stand. Review patient volumes, revenue streams, staffing, and current care workflows.
From there, widen the lens to market trends, competitor moves, and upcoming regulations. Bringing everything together with a SWOT analysis turns a lot of scattered data into a clear starting point.
For example, you may discover solid telehealth adoption alongside outdated billing software. Seeing both strengths and gaps early makes the rest of the plan practical and grounded.
2. Set Clear, Measurable Objectives
Once you know the starting point, define where you want to go.
Broad goals like “improve patient care” sound good, but rarely lead to action. Instead, set specific, measurable targets, such as reducing ER wait times by 15% or increasing chronic care follow-ups within a year.
Then, link every target to a metric and a responsible team. This way, progress is visible and everyone knows what success looks like.
3. Build and Communicate the Strategy
Once objectives are set, lay out the steps, budgets, and timelines to reach them.
The real challenge is making sure everyone understands the plan. So, keep communication clear and practical; think short briefings, simple dashboards, and open Q&A sessions that link the strategy to daily work.
When each team member sees how their role drives the bigger goals, execution gains speed and stays on track.
4. Execute and Monitor Progress
The real test starts when the plan goes live. In this step, track key indicators (patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and revenue) on a regular schedule, such as monthly or quarterly. Use these checkpoints to catch issues early.
For example, if patient satisfaction scores dip, managers can trace the cause and make quick adjustments before it affects retention.
5. Review and Adjust Regularly
Healthcare doesn’t stand still. New technology, changing reimbursement models, and shifting patient expectations can alter priorities overnight.
Build in formal reviews (at least once a year and ideally every quarter) to refresh goals and reallocate resources. This habit keeps your strategy aligned with reality and ready for what’s next.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Even with a solid strategic management plan in healthcare, obstacles can slow progress and test your team’s focus.
Here are the most common challenges and some ways to handle them:
Limited Resources or Budget Constraints
Healthcare budgets are often tight, and new strategic initiatives can look expensive at first glance. The risk is putting off critical updates, like replacing outdated EHR modules or upgrading telehealth platforms, until they become crisis-level issues.
Here’s how to overcome it:
- Prioritize by impact and ROI. Rank projects based on measurable benefits for patients and operations. Then, fund the ones that protect care quality or deliver quick financial returns first.
- Plan in phases. Break large projects into stages so you can launch high-impact pieces while spreading costs over time.
- Seek outside funding. Explore grants, government programs, or partnerships with technology providers. These resources can reduce upfront costs and speed adoption.
Resistance to Change
Change often triggers pushback, even when improvements are clear on paper. Your staff may worry about new technology slowing them down or fear that roles will shift in ways they can’t control.
To fix this, you can:
- Bring staff into the process early. Invite key clinicians, administrators, and even patient reps to planning sessions.
- Show personal wins. Demonstrate how new workflows cut paperwork, simplify scheduling, or improve patient communication.
- Train with purpose. Offer hands-on sessions and quick-reference guides so staff feel confident before launch.
When teams see tangible benefits and feel heard, they’re far more likely to adopt new practices.
Regulatory and Compliance Pressures
Regulations such as HIPAA in the U.S. or GDPR in Europe are complex and always evolving. Missing a change can mean costly penalties and a damaged reputation.
Here’s how you can address this challenge:
- Assign a compliance lead. Make one person or a small team responsible for tracking new rules and coordinating updates.
- Automate documentation. Use software that logs every step of care delivery and generates audit-ready reports.
- Schedule regular compliance checks. Quarterly mini-audits catch gaps before regulators do.
A proactive compliance plan turns a moving target into a manageable routine.
Best Practices for Effective Strategic Management in Healthcare
Strong strategic management takes more than a plan on paper. Actually, it depends on how well it shapes daily actions and delivers measurable results.
These practices can help keep that strategy active and its impact visible:
Engage Leadership and Frontline Staff
A strategy stuck in the boardroom won’t change daily care. So, bring in department heads, physicians, nurses, and key admin staff from the start so everyone owns a piece of the plan.
Also, you can hold short workshops and quick feedback sessions to gather real input before decisions are final. When people see their ideas reflected in the plan, they stay committed and ready to act.
Use Data-Driven Decision Making
Once the right people are engaged, give them solid facts to work with. Track patient outcomes, revenue trends, scheduling metrics, and satisfaction scores so you know what’s working and what isn’t.
Then, share these insights through clear dashboards or brief reports. With the data on the table, leadership can react fast when quality slips or costs rise.
Integrate Technology and Innovation

Data will also reveal where technology can make a difference. Tools like cloud-based EHR systems, telehealth platforms, and AI-driven analytics cut manual work and uncover growth opportunities.
Connect each investment to a specific goal (reducing no-shows, improving chronic care), so every tech upgrade directly supports the strategy you’re driving.
Bottom Line: Put Your Strategic Management Plan in Motion
As you can see, strategic management in healthcare gives clinics and hospitals the structure to stay on course while everything around them changes. The process keeps long-term goals connected to daily work; that way, resources, staff, and patient care stay aligned.
At Medical Flow, we can help you put that system in place. From technology integration to process optimization and compliance support, our team works alongside yours to turn a strategic plan into everyday practice.
Ready to move forward? Connect with us, and let’s build a strategy that keeps care strong and operations ready.
FAQs
What are the five stages of strategic management in healthcare?
These stages are goal setting, analysis, strategy formation, implementation, and monitoring/evaluation. In practice, that means setting clear targets, gathering the right data, choosing a strategy, putting it into action, and checking results to stay on course across the healthcare industry.
What is SWOT analysis in healthcare strategic management?
It’s a simple tool to see where you stand. You list your internal strengths and weaknesses, then look outward at opportunities and threats. The result you’ll get is a clear snapshot that shows where healthcare providers should invest and what risks need a plan.
What role does leadership play in healthcare strategic management?
Leaders set the direction and make sure resources back it up. They also remove obstacles and keep teams aligned, so everyone (from the boardroom to the front desk) moves toward the same goals. All while keeping key stakeholders informed and engaged.
How does strategic management improve patient care and outcomes?
Keeping long-term goals connected to daily work makes care safer and more consistent. With regular check-ins, teams can spot delays, reduce errors, and keep quality high, which leads to better experiences and healthier patients.
How often should a healthcare organization update its strategic plan?
Check key metrics every quarter and refresh the full plan at least once a year. If market conditions or regulations change quickly, update sooner so the plan always reflects reality.
What are the best practices for monitoring and evaluating a healthcare strategic plan?
Focus on a handful of meaningful metrics, review them on a set schedule, and share updates with staff and leadership. Simple dashboards or scorecards make it easy to see progress and act on what the data shows.

 By
By 

