In healthcare, conversational AI is no longer an experiment. Now, it has become a fast-growing industry projected to reach USD 48.87 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of about 23.84 percent.
Behind that number is a clear shift: patients want faster, more precise communication, and clinics can’t scale human teams to meet every query.
Yet, many healthcare providers still treat the usage of AI chats as a side project. They test a bot or a voice assistant, but never connect it with patient records, scheduling, or clinical decision-making. That oversight creates more work for staff and results in a poor patient experience.
Next, we’ll show you how conversational AI works in healthcare, where it’s already solving real problems, and what benefits and challenges to expect. If you run a clinic or health network, these insights will help you plan the next move.
Let’s take a look, shall we?
- TL;DR
- What Conversational AI in Healthcare Is
- How Conversational AI Works in Healthcare
- Main Use Cases of Conversational AI in Healthcare
- Key Benefits for Providers and Patients
- Challenges and Considerations of Conversational AI in Healthcare
- What’s the Future Outlook for Conversational AI in Healthcare?
- Ready to Bring AI into Everyday Care?
- FAQs
TL;DR
Short on time? Here are the main takeaways:
- Conversational AI is changing how clinics and health networks communicate with patients.
- It handles routine tasks like booking, follow-ups, and education so staff can focus on complex care.
- Clinics gain faster workflows and stronger patient engagement when AI is fully integrated with EHR and telehealth systems.
- Success depends on strong privacy compliance, reliable integrations, and patient trust from day one.
- Early adopters are already using it to improve treatment planning, chronic care, and operational efficiency.
What Conversational AI in Healthcare Is
For starters, conversational AI is a technology that lets people interact with computers naturally, using text or voice instead of commands or menus. You probably have seen it already in virtual assistants, customer service chats, and voice apps in many industries.
In healthcare, this AI takes on tasks like scheduling visits, giving clear medication guidance, or helping someone decide if they need a check-up.
Unlike a basic FAQ bot, it keeps track of context, improves with every conversation, and connects directly with electronic health records or scheduling systems.
The goal of this tech isn’t to replace doctors. Actually, it aims to handle routine work so medical staff can focus on care that requires human judgment.
Core Elements Behind the Technology
Some key building blocks of conversational AI include:
- Natural language processing (NLP): Converts patient questions into structured data for accurate analysis.
- Machine learning and LLMs: Improve accuracy with each interaction.
- Integration layers: Secure APIs connect AI with electronic health records (EHRs), scheduling tools, and billing systems.
- Compliance and security frameworks: Encryption, audit trails, and access controls aligned with HIPAA and GDPR.
Together, these layers enable precise, personalized support rather than canned responses.
Its Role Inside Today’s Healthcare System
Nowadays, conversational AI is becoming part of daily care. Patients get quick answers and help any time of day: checking symptoms, reviewing a treatment plan, or getting a nudge to take their medication. All without waiting on the phone.
For clinics and health networks, it’s a way to serve more people without overloading staff. This AI can book appointments, handle insurance questions, and follow up after visits, while every conversation feeds data back for smarter decisions.
Hospitals, small practices, and telehealth teams are already using it to cut missed appointments, lower admin costs, and keep chronic care on track.
With patient expectations rising and staff stretched thin, this technology is moving from a nice option to a basic part of how care gets delivered.
How Conversational AI Works in Healthcare
Conversational AI moves from a patient’s question to an action in the clinic with a few precise steps. Here’s how that flow unfolds:
From Patient Question to AI Understanding
It begins with a patient typing a chat or speaking on the phone. Natural language processing (NLP) turns that message into data the system can read.
Then, large language models (LLMs) add context and catch medical terms, so the AI knows if it’s a simple booking or a possible urgent issue.
Turning Insights Into the Right Action
Next, the AI decides what needs to happen. It can confirm an appointment, send prep instructions, or pass the case to a doctor for review.
Built-in clinical rules and local compliance checks keep every step safe and aligned with medical standards.
Answer Delivery Through Connected Systems
The response shows up where it matters (text, email, or patient portal) while updating the electronic health record and scheduling tools in the background. Everyone sees the same information in real time, which means no missed notes or double entries.
Continuous Improvement Through Feedback
Every conversation teaches the system something new. It reviews accuracy and patient feedback, then fine-tunes future answers. Over time, the assistant gets sharper without needing constant reprogramming from your team.
Main Use Cases of Conversational AI in Healthcare
Here’s where clinics and health networks are already putting this tech to work:
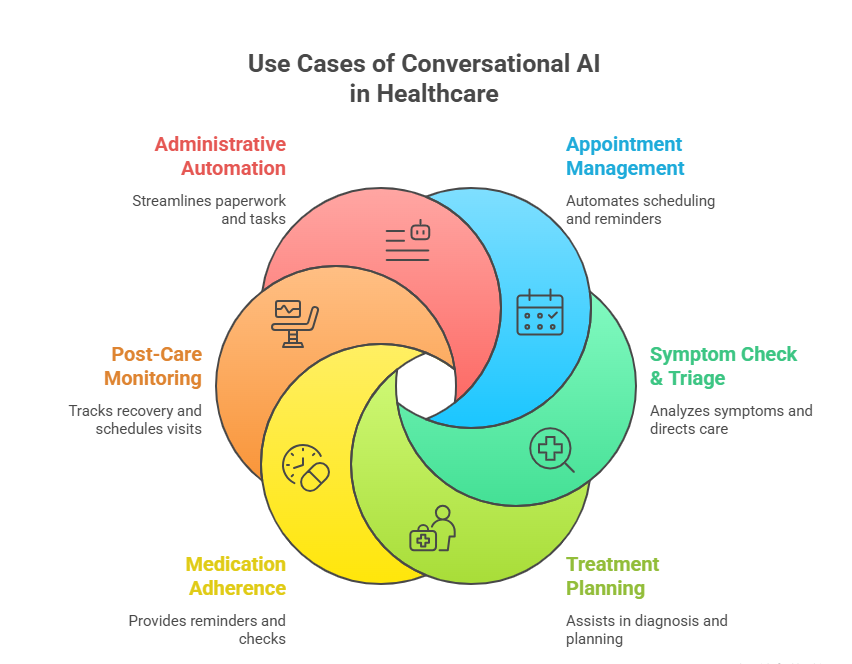
Appointment and Follow-Up Management
An AI assistant can handle bookings from start to finish. It confirms visits, sends prep tips, and nudges patients with reminders so they actually show up.
If someone cancels, it can rebook the slot automatically, keeping your calendar full and your staff focused on care.
Symptom Check and Triage Support
Patients can share how they feel in simple words. Then, the AI analyses their description, checks severity, and points them to the right care; be it self-care advice, a same-day appointment, or urgent attention.
This quick sorting helps real emergencies get seen faster and keeps minor cases out of overcrowded ERs.
Treatment Planning
Designing a treatment plan involves a lot of moving parts: drug interactions, follow-up schedules, and the latest clinical guidelines. And conversational AI is starting to ease that load.
Recent data highlights how quickly doctors are adopting these tools. A survey by Fierce Healthcare found that over 60% of doctors use large language models to check drug interactions, more than half for diagnoses, and about 40% for treatment planning.
Also, this trend already shows real impact. A strong example is Cedars-Sinai’s CS Connect, which has supported about 42,000 patients, and 77 percent of its AI treatment suggestions were rated optimal, compared with 67 percent for physicians in similar cases.
These numbers show how well-trained AI can reinforce medical decisions and help create safer, more consistent care plans.
Medication Adherence and Reminders
Sticking to a prescription is harder than it sounds. Patients forget doses, run out of refills, or stop medication when side effects appear.
Conversational AI tackles these gaps in real time. It sends clear, timely reminders that fit each patient’s schedule and checks in with simple questions like “Did you take your dose today?”
If a patient reports missed pills or side effects, the system can flag the care team instantly or suggest a follow-up call.
For clinics, this means fewer treatment gaps and better long-term results. And, for patients, it’s steady support that keeps their care plan on track without extra visits.
Post-care and Remote Monitoring Support
After discharge, AI chats keep patients connected. It tracks recovery signals, asks the right follow-up questions, and books a virtual visit if something looks off. That early warning can lower readmissions and give patients peace of mind at home.
Administrative Task Automation
AI can also lighten back-office work. It drafts visit notes, files insurance claims, and updates records automatically. As Fierce Healthcare also noted, nearly half of physicians already use AI to create clinical documentation.
Less paperwork means more time with patients and fewer late nights finishing charts.
Key Benefits for Providers and Patients
Conversational AI goes beyond being a convenience feature. When it’s planned and connected to core systems, it creates measurable wins for both clinics and the people they care for.
Some of those wins include:
Better Patient Experience
Fast answers build trust. Patients can book appointments, get treatment instructions, or ask about side effects at any time of day. They don’t have to wait on hold or repeat information to multiple staff members.
This ongoing dialogue also keeps patients engaged between visits. Hybrid chatbots, for example, have been shown to reduce hospital readmissions by up to 25%, improve patient engagement by 30%, and cut consultation wait times by 15%.
All of that adds up to better outcomes and higher satisfaction scores.
Greater Operational Efficiency
Every task the AI takes off staff’s hands frees time for direct care. Appointment scheduling, documentation, insurance follow-ups, and basic patient education can all be automated.
This lowers administrative costs and helps teams manage more patients without hiring extra staff.
Stronger Insights From Patient Data
Since every interaction is digital, clinics gain a continuous feed of structured data. Over time, it shows patterns in symptoms, medication use, and service demand.
Clinics can use this to improve care plans, plan staff, and keep supplies ready.
Challenges and Considerations of Conversational AI in Healthcare
The potential of this technology in healthcare is clear, but implementation takes planning. Clinics that jump in without a framework run into problems that slow adoption and hurt patient trust.
Some challenges include:
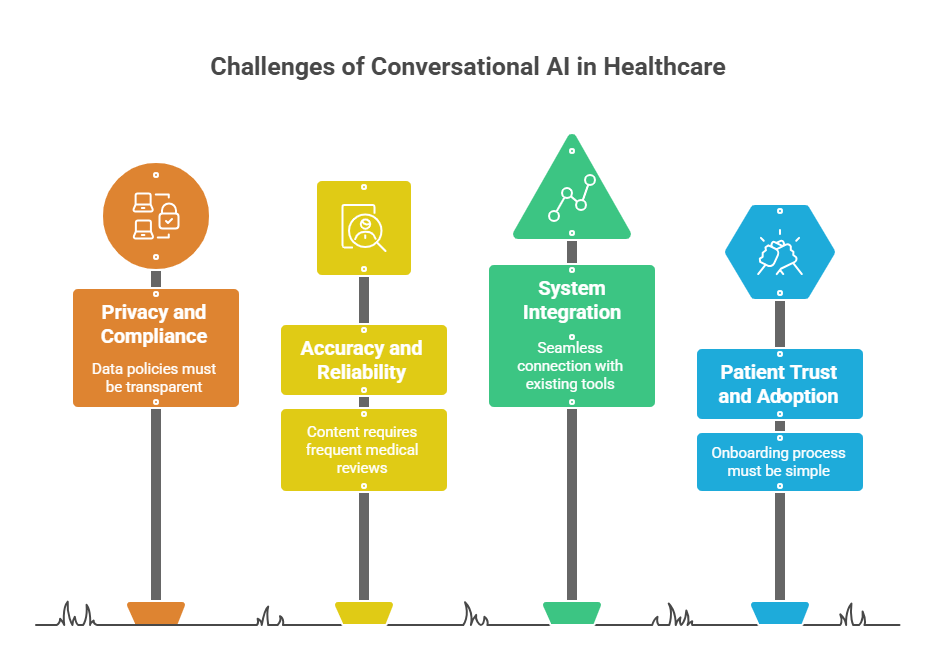
Privacy Protection and HIPAA Compliance
Patient data is sensitive and tightly regulated. For that reason, conversational AI must meet HIPAA, GDPR, and local privacy requirements. That includes encrypted data flows, secure authentication, and clear policies on how information is stored and shared.
Accuracy and Reliability
Health advice has to be right the first time. An AI model trained on outdated or low-quality data can give unsafe guidance.
That’s why providers need a process to review and update medical content, along with a clear handoff to human clinicians when a case goes beyond AI limits.
Smooth Integration with Existing Systems
Conversational AI needs to connect smoothly with EHR, scheduling, and billing tools. With secure links and real-time updates, information flows automatically. That way, staff and patients always have the right details without extra data entry or workflow changes.
Patient Trust and Adoption
Patients need confidence that an AI assistant is safe and helpful. That’s a bigger challenge than many expect. In fact, only about 10% of patient interactions with healthcare conversational AI are fully self-serve today.
To address this, make the first steps simple, spell out privacy clearly, and keep every message easy to read. That’s how patients feel confident and keep using the service.
What’s the Future Outlook for Conversational AI in Healthcare?
Indeed, conversational AI is still early in its curve. But the next phase is already taking shape:
Advances in Natural Language Understanding
Language models keep getting sharper. Soon, AI assistants will handle nuanced medical questions and regional speech with near-clinician accuracy. They’ll pick up on subtle symptoms and context, giving patients clear answers without constant human review.
Deeper Links With Wearables and IoT
Smart devices are everywhere, from heart monitors to glucose sensors. The next generation of conversational AI will pull live data from these tools and connect it to care plans.
Just imagine this scenario: A patient might report chest discomfort, and the AI will instantly check heart-rate trends before recommending next steps.
Expansion Toward Preventive and Personalized Care
The future is about anticipating needs instead of a fast response. Conversational AI will help spot early risk factors, send lifestyle prompts, and adapt guidance to each patient’s health history.
Key insight: As noted by McKinsey & Company, healthcare leaders are already investing heavily in AI solutions such as chatbots, conversational AI, and virtual assistants to stay relevant and competitive.
Ready to Bring AI into Everyday Care?
Patient needs are growing, and clinic teams already have full plates. But, as you could see, conversational AI can help to close that gap. Clinics using it now are already cutting admin time, improving follow-ups, and keeping patients engaged between visits.
At Medical Flow, we can help you get there without unnecessary detours. We guide platform selection, connect the AI with your EHR and scheduling tools, train your team, and stay involved so the system keeps improving.
If you’re ready to reduce admin load and offer patients quicker, smoother care, let’s talk. We can set up an AI service that starts strong and keeps improving.
FAQs
What is conversational AI in healthcare?
It’s a smart chat or voice system that lets patients talk with clinics in everyday language. They can ask questions, book visits, or get treatment info while the system keeps their personal data safe and improves overall patient care.
Is conversational AI the same as a chatbot?
No. A simple chatbot only gives set answers. Conversational AI can understand context, pull patient details when needed, and improve its responses over time, making it one of today’s most practical AI technologies for health services.
How are AI chatbots used in healthcare?
They help people book and change appointments, check symptoms, get reminders to take medicine, and stay in touch after a hospital visit. Many doctors also use them to double-check drug interactions or draft notes.
Which healthcare providers benefit the most?
Any clinic, hospital, or telehealth service that wants to cut paperwork and give faster answers can benefit. Busy healthcare organizations with high call volumes see results especially quickly.
Can conversational AI connect with EHR or telehealth tools already in place?
Yes. With the right setup, it links directly to scheduling, billing, and electronic health records so everyone sees the same up-to-date information, improving the user experience for staff and patients.
How secure is patient data with conversational AI?
Patient privacy is a top priority. Well-built systems use strong encryption, limit access to authorized staff, and follow rules like HIPAA and GDPR to keep medical data safe while using artificial intelligence responsibly.
What are the downsides of conversational AI in healthcare?
It needs careful planning and clear processes to work well. Without properly implementing conversational AI steps and patient education, people may avoid using it, and only a small share of interactions may run fully on their own.

 By
By 




