
AI and IoT keep showing up in the same room, and it’s not by chance. Clinics need faster decisions, fewer manual steps, and better visibility between visits.
Connected devices show what’s happening in real time. AI makes sense of it. Together, they turn raw signals into insights your team can use.
That matters in healthcare, where nothing stands still. Patients move between home, clinics, and hospitals. Staff switch systems constantly. Data flows across platforms that don’t always talk to each other.
But when that chain breaks, things slow down, gaps appear, and time gets wasted.
AI and IoT in healthcare solve that disconnect. They create a layer where sensors, software, and decisions work together, so care and operations don’t depend on patching things manually.
And adoption is already moving. By early 2025, 70% of payers and providers were investing in generative AI. Meanwhile, over 60% of hospitals had IoT devices in place.
So, let’s see how these systems connect and what that means for how your team works.
- TL;DR
- AI and IoT in Modern Healthcare Systems: What Is Their Role?
- How AI and IoT Combine in Healthcare Systems
- Core Use Cases of AI and IoT in Healthcare
- Business and Clinical Value for Healthcare Providers
- AI and IoT Adoption: What Challenges Must Healthcare Organizations Address?
- Technical Foundations of AI and IoT in Healthcare
- Ethical and Legal Considerations of AI and IoT in Healthcare
- How Healthcare Organizations Can Approach the Adoption of AIoT
- Bottom Line: Make AI and IoT Work Together
- FAQs
TL;DR
If you want the short version, here it is:
- IoT in healthcare captures continuous patient and facility data through connected devices.
- Meanwhile, AI in healthcare turns that data into predictions, prioritization, and automation that reduce delays and manual work.
- AIoT is the bridge: IoT collects, AI interprets, and AIoT pushes actions closer to the point of care for speed and scale.
- Adoption is real: 63% of healthcare professionals surveyed were already using AI, and 31% were piloting or assessing.
- At scale, connected care is already serving tens of millions: telemedicine + IoT platforms support daily routines for ~76 million patients.
- The payoff shows up in operations: organizations report IoT-driven cost reductions and expect impact on outcomes and efficiency.
- The risk is also real: privacy, interoperability, and clinical trust can stall adoption if you don’t plan for them early.
AI and IoT in Modern Healthcare Systems: What Is Their Role?
AI and IoT don’t play the same role in healthcare, but they’re tightly connected. One interprets, and the other observes. And neither delivers much value on its own.
To see how they work in practice, it helps to look at each layer separately before connecting them:
AI 101 in Healthcare: Understanding AI, Cloud Computing, Edge & IoT Integration | Session 1.26
Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
AI is already embedded in how care gets delivered and how clinics stay operational. It usually shows up in two areas: clinical support and operational execution.
On the clinical side, AI helps teams prioritize and act faster. Common applications include:
- Predictive analytics: Such as identifying patients at risk of deterioration, no-shows, or readmission.
- Decision support: Like flagging clinical risk, prioritizing outreach, or surfacing relevant patient history.
- Automation: Including draft notes, task routing, and reduction of repetitive admin work.
On the operational side, AI targets friction that slows everything down. That usually means:
- Triage queues that grow without visibility.
- Referral bottlenecks between departments or providers.
- Scheduling that breaks under real patient behavior.
- Billing workflows that depend on perfect documentation.
Adoption is accelerating, but it’s uneven. A 2025 industry report by NVIDIA shows healthcare leading other industries, with 63% already using AI and another 31% piloting or assessing initiatives.
So yes, AI is quickly becoming the baseline. But the real choice is where you start, so tools reinforce how your team works instead of creating more gaps.
Medical AI: Benefits of new technology and use case examples of AI in health care
Internet of Things in Healthcare
If AI interprets, IoT observes. It’s what captures what’s really happening; continuously, automatically, and without extra work from your team.
In healthcare, IoT means connected devices collecting clinical and operational data in the background. Think of things like:
- Wearables track heart rate, sleep, SpO2, activity, or ECG.
- Home monitoring devices like blood pressure cuffs, glucose monitors, scales, and pulse oximeters.
- Hospital equipment sensors report utilization, location, status, or maintenance signals.
- Facility sensors monitor temperature, humidity, assets, and patient flow.
This stream of data changes how teams work every day. It helps them:
- Intervene earlier instead of reacting late.
- Reduce blind time between visits.
- Spot equipment issues before they cancel appointments.
- Coordinate staff and rooms with fewer manual steps.
The scale is already significant. According to SQ Magazine, healthcare IoT devices surpassed 540 million units, with remote patient monitoring as the dominant use case.
Still, more devices don’t automatically improve care. When data lands in multiple dashboards with no prioritization, teams tend to ignore it.
And that gap is what sets the stage for AIoT.
AIoT: The Operational Layer Between AI and IoT
AI and IoT, on their own, each solve part of the puzzle. But when they stay in separate lanes, care teams still have to connect the dots manually.
Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) bridges that gap. It’s the layer that turns raw data into real-time action and is closer to where care is happening.
AI + IoT: How Artificial Intelligence Is Redefining the Future of Technology
Here’s how it works in practice:
- IoT devices send continuous signals from patient monitors, medical equipment, and facility sensors.
- AI processes those signals to detect risks, spot trends, and surface what actually needs attention.
- AIoT turns those insights into action, like sending alerts, triggering tasks, or updating care plans automatically.
Speed is what makes this work. If every datapoint has to travel to the cloud and back, alerts lag, and decisions stall. Processing closer to care reduces delays and keeps everything moving.
And this is already happening. According to SQ Magazine, IoT-integrated telemedicine platforms now support daily routines for over 76 million patients worldwide.
In short: IoT shows what’s happening. AI explains it. And AIoT makes sure that the explanation reaches the right place, at the right time.
How AI and IoT Combine in Healthcare Systems
Once devices and intelligence are connected, the focus shifts from tools to flow. Data moves from capture to action without waiting for manual steps.
That’s where care teams start seeing real impact.
Here’s how the pieces come together inside day-to-day operations:
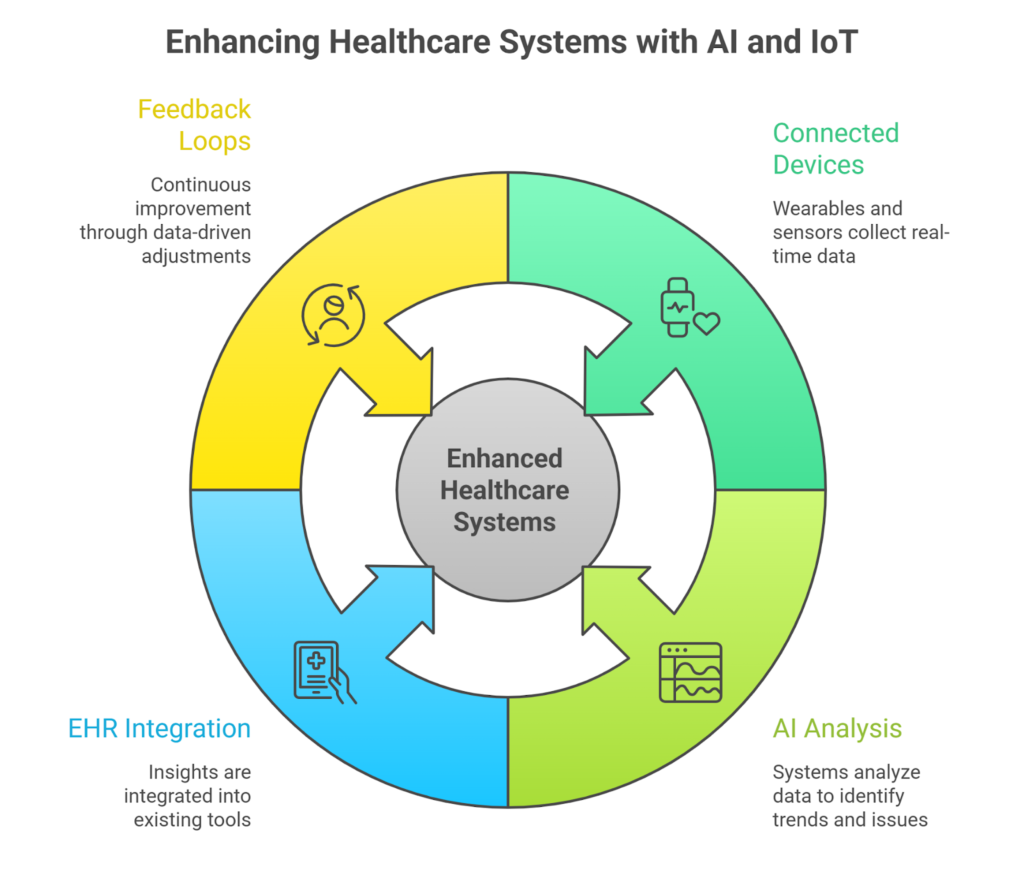
Data Capture from Connected Devices
Everything starts at the edge. You have wearables, home monitors, medical devices, and facility sensors working in the background, capturing patient and operational data in real time.
This flow covers vitals, activity patterns, device performance, room usage, and environmental signals. But what matters here is consistency.
Data comes in continuously, not only during clinical visits, which helps you avoid blind spots between one encounter and the next.
Real-Time Analysis and Signal Detection
Raw data isn’t helpful on its own. AI systems analyze incoming streams to spot patterns, trends, and anomalies as they happen.
With AIoT, much of that happens right where the data is created, which speeds things up and avoids overloading teams with irrelevant alerts.
Clinical and Operational Decision Support
Once signals are prioritized, they go straight into the systems your team already uses. Be it EHRs, dashboards, or scheduling tools.
That way, care teams act faster, admin teams catch issues earlier, and decisions land with the context they need.
Closed-Loop Feedback Across Systems
Every action taken by staff feeds back into the system. With time, this creates a steady learning loop:
- Thresholds fine-tune themselves.
- Alerts become more accurate.
- Workflows feel more predictable.
- Performance gaps narrow without the need for constant manual adjustments.
That closed loop is what truly separates connected systems from basic monitoring tools. It also lays the groundwork for the real-world use cases teams rely on every day.
Core Use Cases of AI and IoT in Healthcare
Once AI and IoT are working together, use cases stop being theoretical. They show up in everyday workflows that affect patient experience, staff workload, and operating costs.
Across healthcare providers, these are the use cases you see most in practice:
- Remote patient monitoring: Teams can track vitals and symptoms outside the clinic, without depending on constant in-person visits. This helps them act sooner and reduce appointments that don’t bring clinical value.
- Chronic condition support: For patients with diabetes, heart failure, or COPD, continuous monitoring combined with AI-driven alerts keeps care teams informed. All without disrupting daily life.
- Early risk identification: By analyzing changes in behavior or health data, systems can flag signs of deterioration, missed treatments, or readmission risk before they escalate.
- Predictive equipment maintenance: Sensors track how equipment is used and detect wear in real time, so service happens before breakdowns. That avoids downtime and helps staff rely on the tools they need.
- Smart hospitals and connected facilities: Real-time data on beds, rooms, assets, and patient flow makes coordination between departments faster, smoother, and less reactive.
- Workflow coordination and resource allocation: With better data, teams can plan staffing and schedules more accurately. It’s easier to allocate resources with confidence instead of reacting under pressure.
Behind all of these use cases is the same foundation. Data flows continuously, is processed quickly, and leads to action without creating extra work for staff or friction for patients.
Key Insight: 81% of U.S. clinicians report using remote patient monitoring (RPM), a sign of how connected care tools have moved into practice.
Business and Clinical Value for Healthcare Providers
Once AI and IoT are connected, the value shows up fast. You see it in shorter response times, clearer priorities, and systems that fit how your teams work day to day.
This is where connected systems start being useful:
Better Patient Outcomes
When monitoring is continuous, and signals are prioritized correctly, care becomes more proactive. Teams intervene earlier. Patients feel supported between visits instead of forgotten.
That expectation is shared at the leadership level. According to Market.us, around 75% of healthcare executives believe IoT will significantly impact patient outcomes and operational efficiency. The link is simple: better visibility leads to better timing.
Faster Clinical Response
In healthcare, speed is critical. Delays frustrate staff, and they can put patients at risk.
AIoT shortens the gap between signal and action. Teams don’t need to sift through raw data. They get alerts with context, right when it counts. That means quicker decisions and less mental overload.
Lower Operational Friction
Disconnected tools slow everything down. Manual handoffs slow teams down. Information gets entered more than once. And staff spend time jumping between tools just to find what they need.
AI and IoT fix that by keeping tasks and information moving in sync. Teams spend less time chasing details and more time moving things forward.
The impact shows up in the numbers. Facilities using IoT report a 26% drop in operational costs on average, as Market.us also stated.
When systems talk to each other, the inefficiencies are easier to spot and easier to fix.
Stronger Data-Driven Decisions
Healthcare generates massive amounts of data. The challenge is making it useful.
With AI in place, teams can finally see patterns, spot risks earlier, and stop reacting to problems after the fact. It shifts the whole conversation from catching up to staying ahead.
More Efficient Use of Staff and Resources
Tech alone won’t fix staffing shortages. But better coordination changes how far teams can go.
AI and IoT help align schedules, equipment, and patient needs, so time isn’t wasted in one place while another is overloaded.
That kind of efficiency matters. Industry forecasts suggest AI could cut hospital operating costs by 10–20% over time, translating into hundreds of billions in potential savings long term.
Key Insight: 78% of healthcare executives in the U.S. now report that AI integration is essential to their digital transformation strategies, reflecting the priority many organizations place on AI beyond experimentation.
AI and IoT Adoption: What Challenges Must Healthcare Organizations Address?
Even with clear benefits, AI and IoT adoption don’t always move smoothly. Most teams run into the same set of problems once they try to scale beyond pilots.
Knowing where the friction shows up helps you deal with it early:
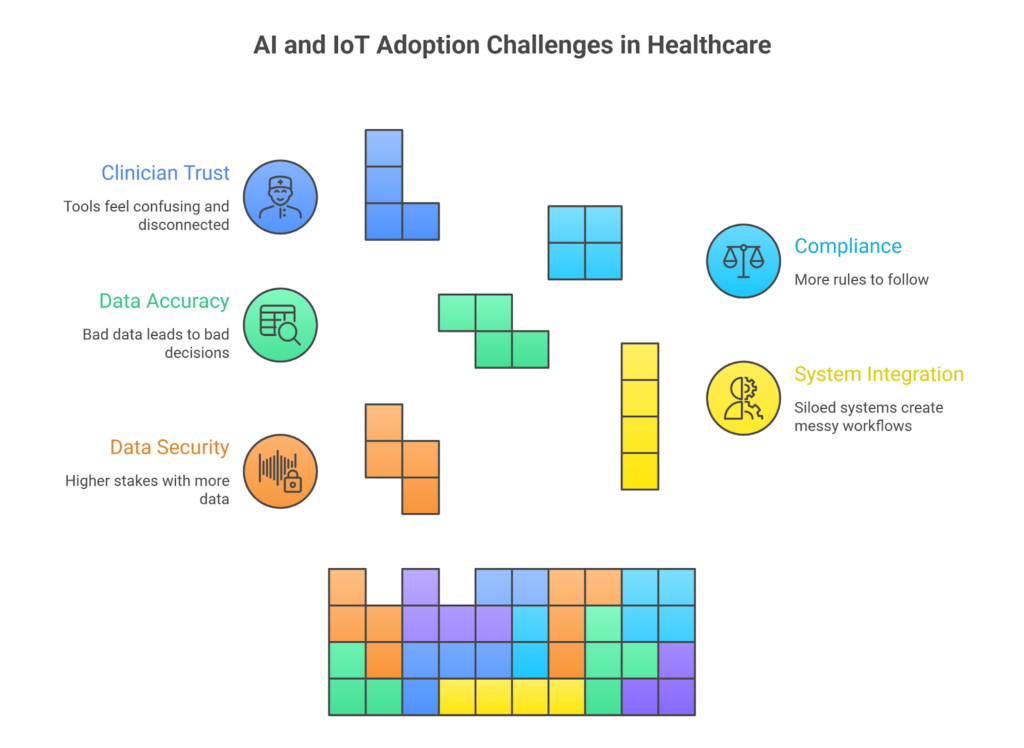
Data Privacy and Security Exposure
More connections mean more data in motion, across systems, vendors, and devices.
Without the right controls in place, security risks start to build up quietly. That’s why system design needs to account for privacy from day one, not after launch.
Interoperability Between Systems
Many healthcare tools were never meant to work together. IoT devices, AI platforms, EHRs, and older systems often run in parallel.
When integration falls short, teams end up juggling workflows and repeating tasks. Key information gets missed, and work slows down.
Data Accuracy and Reliability
AI is only as good as the data behind it. Gaps, inconsistencies, or faulty device readings lead to bad calls.
Not every signal needs action, and not every alert should be escalated. Systems need to be validated and earn trust before anyone relies on them.
Regulatory and Compliance Pressure
The rules haven’t gone away; if anything, connected systems add complexity.
Data may cross borders, vendors may access sensitive info, and when responsibilities aren’t clear, decisions stall. Strong governance and documentation help teams move forward without second-guessing every step.
Clinical Trust and Adoption
If clinicians don’t trust the system, it doesn’t matter how advanced it is.
And that’s the real barrier. Deloitte’s 2026 outlook found that only 30% of health systems are using generative AI at scale, despite strong interest. What holds them back isn’t lack of ambition; it’s hesitation around how these tools work in real clinical settings.
Adoption improves when tools fit naturally into the workflow, make their logic visible, and support clinical judgment.
That’s not a knock on AI’s potential. It just explains why adoption looks slower than the headlines suggest.
Technical Foundations of AI and IoT in Healthcare
For AI and IoT to work together in healthcare, the technical foundation has to be stable and predictable. This layer isn’t always visible, but it determines how well connected systems hold up once they move beyond pilots.
Most issues here appear later, when data volume increases and workflows begin to rely on continuous data flow.
Let’s see which are the most common:
Devices, Sensors, and Edge Infrastructure
This is where the data starts. Wearables, home monitors, medical devices, and facility sensors generate information at the edge, before it ever reaches the cloud.
To be useful, these tools need to be accurate, consistent, and comfortable enough for patients to use over time. Edge processing helps move that data faster, keeping care decisions timely and operations responsive.
Data platforms and cloud architecture
Once data leaves the edge, it needs an environment that can handle scale and complexity. Healthcare data comes in fast, from many sources, and in different formats.
Cloud infrastructure has to manage that flow without bottlenecks, silos, or downtime. Why? Because if access fails, care workflows stall too.
AI models and analytics layers
This is where signals become insight. AI models scan incoming data to detect risks, spot patterns, and help teams focus.
But they need well-defined inputs and performance metrics to stay reliable, and they can’t run on autopilot. Ongoing monitoring ensures they don’t drift over time, especially as patient populations change.
Integration with EHRs and clinical systems
Insights only help when they land where people actually work. If alerts live in separate dashboards, they get ignored.
The goal here is to route key information straight into the systems teams already use: EHRs, care coordination tools, or task lists. That way, acting on it doesn’t feel like extra work.
Ethical and Legal Considerations of AI and IoT in Healthcare
As systems become more connected, performance isn’t the only thing that matters. Trust, clarity, and responsibility have to be built in from the start.
Here’s what to pay attention to:
- Patient consent and data control. When data flows nonstop, consent can’t be a one-time checkbox. Patients need to know what’s being collected, how it’s used, and who has access.
- Transparency and explainability. If AI makes a recommendation, teams need to understand why. And patients want to know that decisions aren’t random. This is about making the reasoning clear enough to trust.
- Bias, accountability, and clinical responsibility. AI learns from data. And if that data is incomplete or biased, it affects the outcome. The tech can help, but the responsibility still falls on people. Clear roles and governance help make sure no one’s left guessing.
- Staying aligned with regulations. The rules haven’t changed, but the tech has. Data moves across systems, vendors, and sometimes borders. That makes things like access control, documentation, and audit trails more important than ever.
Handled well, these considerations don’t slow progress; they make it sustainable.
How Healthcare Organizations Can Approach the Adoption of AIoT
Adoption works best when it’s structured and focused. Most successful implementations don’t start big but start with one clear objective.
This approach reduces risk and builds confidence without overwhelming teams:
- Clear use case definition: Focus on a specific clinical or operational problem with measurable impact.
- Data readiness and infrastructure review: Make sure existing data sources are accurate, accessible, and reliable.
- Vendor and partner evaluation: Prioritize integration, compliance support, and long-term fit.
- Pilot programs and validation: Use small pilots to test assumptions and surface workflow issues early.
- Clinical enablement and change management: Adoption improves when teams see how tools support their work.
Key Insight: Adoption priorities vary by region. Deloitte’s outlook also shows that 37% of US health system executives expect AI to be a major focus, compared with 22% outside the US. A staged approach helps balance ambition with readiness.
Bottom Line: Make AI and IoT Work Together
AI and IoT are already in use across healthcare. The difference comes from how intentionally they’re connected.
When systems work together, teams get clearer signals, respond faster, and spend less time chasing information. Care feels more continuous, even outside the clinic.
You don’t need to change everything at once. You need to be clear about where connected systems add value and make sure they fit existing workflows.
At Medical Flow, we work with healthcare providers to design and implement connected care models that make sense operationally and stay compliant.
If you’re deciding how AI and IoT should work in your organization, let’s talk and see how connected care can work for you.
FAQs
What is the Internet of Things (IoT), and how is it related to healthcare?
IoT refers to connected devices that collect and share information automatically. In the healthcare sector, this includes wearables, home monitors, and equipment sensors.
These tools help teams see what’s happening in real time, without relying on manual input or in-person visits.
How does artificial intelligence (AI) support healthcare systems?
AI helps teams make sense of the patient data they already have. It spots patterns, flags risks, and gives context to help with faster, better decisions. From triage to admin workflows, it’s about helping (not replacing) the people delivering care.
How are AI and IoT reshaping modern healthcare systems?
Together, they solve two key problems: lack of visibility and slow response. IoT captures what’s happening. AI helps decide what to do about it. That means less chasing data, fewer delays, and systems that feel more connected to how care happens.
What are the applications of AI and IoT in healthcare?
They show up in real workflows like remote patient monitoring, risk detection, scheduling, medical image analysis, equipment tracking, and care coordination. Anywhere timing matters, or teams need to do more with less, AI and IoT can help.
How do AI and IoT work together to enable remote patient monitoring?
IoT devices collect vital signs and other health data generated by IoT sensors outside the clinic. Meanwhile, AI looks for patterns and signals that matter.
That way, teams can enhance patient care by stepping in early. All without waiting for the next appointment or relying on patients to report every detail manually.
What are the key challenges in integrating AI and IoT in healthcare?
The tech only works if it fits the reality on the ground. That means getting the medical data right, making systems talk to each other, and protecting data security from the start. The integration of AI also has to support real workflows, not just add complexity.






